Introduction
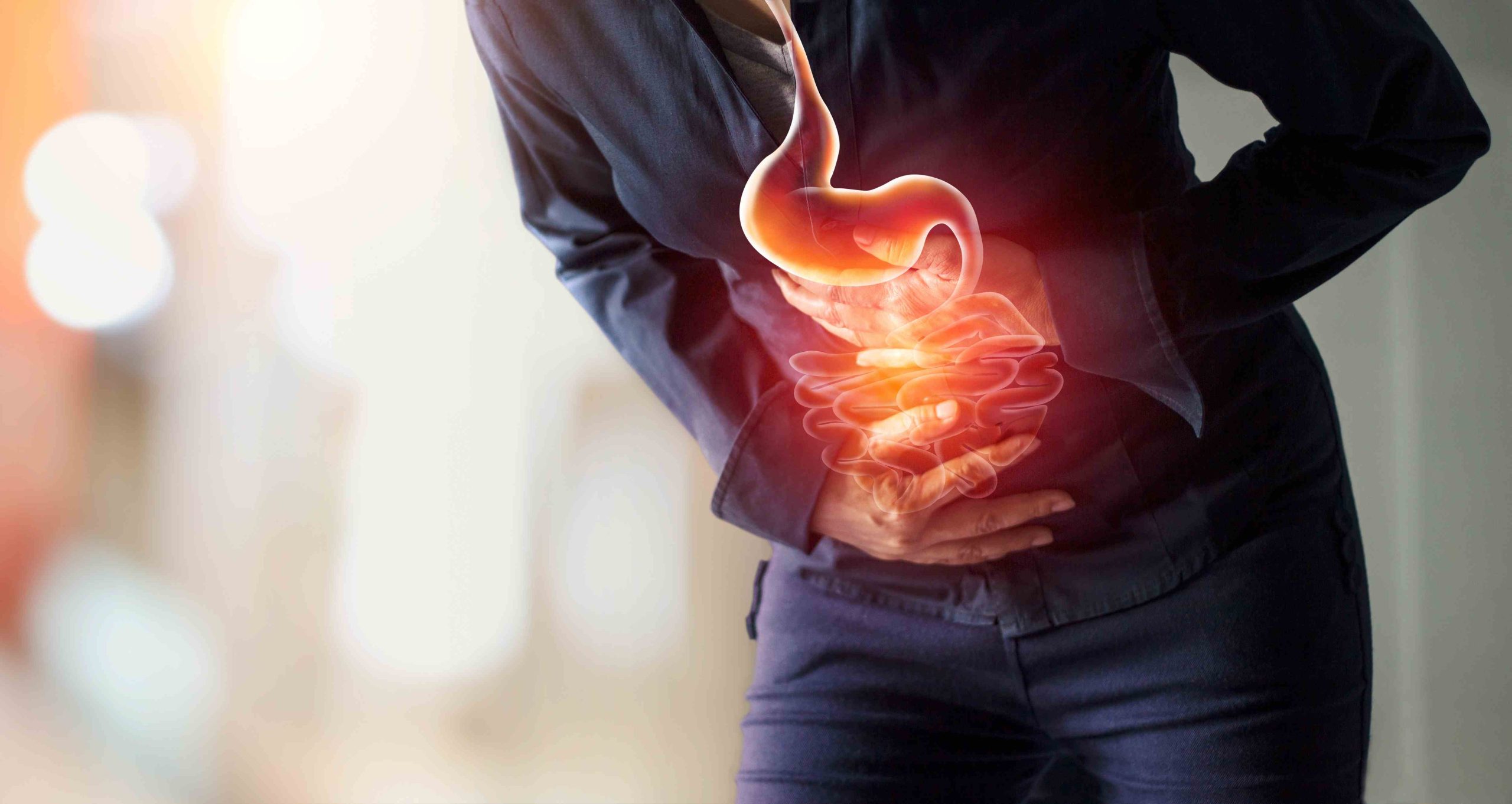
Experiencing excess stomach gas can be uncomfortable and even embarrassing. While it’s a common issue, certain medical treatments and lifestyle choices can exacerbate this condition. In this article, we will delve into 10 treatments that can potentially cause excess stomach gas and provide practical tips on how to manage it effectively.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, but they can also disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to increased gas production. To counteract this effect, consider incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt or kefir into your diet during and after antibiotic treatment.

Fiber Supplements
While fiber is crucial for digestive health, consuming excessive amounts in the form of supplements can lead to increased gas production. Gradually introduce fiber supplements to allow your digestive system to adapt. Additionally, stay well-hydrated to help prevent gas and bloating.

Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, are commonly used to relieve pain and inflammation. However, they can irritate the stomach lining, potentially leading to increased gas production. If possible, consult with your healthcare provider about alternative pain management options.
Chemotherapy
Cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, can affect the digestive system and lead to excess gas. Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and incorporating gentle physical activity can help alleviate discomfort.
Chemical laxatives
While laxatives can provide relief from constipation, some types can lead to excess gas. Opt for natural remedies like prunes, increased water intake, and regular exercise to promote regular bowel movements.

Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners like sorbitol, xylitol, and mannitol are common culprits for excess gas. Read labels carefully and limit consumption of products containing these sweeteners.

Carbonated Beverages
Carbonated drinks introduce air into the digestive system, leading to increased gas. Opt for non-carbonated alternatives like herbal teas or infused water to quench your thirst.

Dairy Products
Lactose intolerance, a condition where the body has difficulty digesting lactose found in dairy products, can lead to excess gas. Experiment with lactose-free alternatives or consider enzyme supplements to aid digestion.

Surgery and Anesthesia
Certain surgical procedures and the use of anesthesia can temporarily slow down the digestive system, potentially leading to excess gas post-surgery. Gradually reintroduce solid foods and engage in light physical activity to stimulate digestion.
Gluten-containing Foods
For individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, consuming gluten can lead to digestive discomfort, including excess gas. Opt for gluten-free alternatives like rice, quinoa, and gluten-free grains.

Conclusion
Experiencing excess stomach gas can be a common side effect of various medical treatments and lifestyle choices. However, understanding the underlying causes and implementing practical strategies can significantly alleviate discomfort. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific situation. Remember, managing excess stomach gas is an important step towards maintaining overall digestive health and well-being.